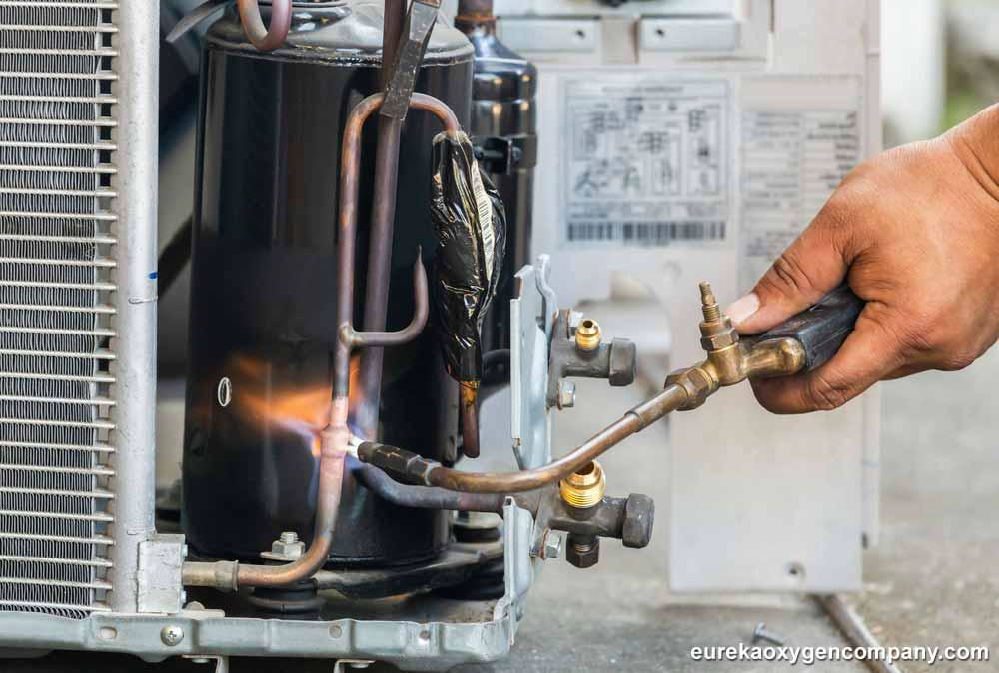The term industrial gases is a broad term that encompasses a wide variety of gases which are used in diverse industrial applications. Most of these products are in gaseous form at room temperature as well as pressure. However, they can still be stored in either liquid or solid form, though many are commonly utilized in their gaseous state. Ideally, industrial gases are considered to be valuable for either their reactivity, inertness, or coldness. These given properties are carefully exploited in a variety of applications in different industries.
Industrial gases consist of elements, mixtures, or molecular compounds. Some of the most common gases of this kind include oxygen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and nitrogen, not to mention noble gases like argon, xenon, neon, and krypton. A number of industrial gases including oxygen, nitrogen, argon, LNG, and LPG are liquefied under great pressure for efficient storage and transportation. Alternatively, dry ice, the frozen form of the gas carbon dioxide, is an excellent example of a gaseous material which is valuable in its solid state. While gases like hydrogen are known to be extremely volatile and necessitate specialized handling and storage to guarantee safe utilization. Let us now take a look at the most common groups of industrial gases currently made available in the market.
Flammable gases
Flammable gases are those which when mixed together with air or oxygen in ideal concentrations will either burn or explode once brought into contact with an ignition source. Some of the most common of these industrial gases include acetylene, butane, isobutane, hydrogen, arsine, ethane, ethylene, and methane.
Inert gases
Otherwise known as noble gases, this group of industrial gases can’t react with other materials in their proximity and can’t participate in combustion processes either. Some notable examples of inert gases include argon, helium, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, neon, xenon, propane, silane, and propylene.
Hydrocarbon gases
This class of industrial gases are mixtures of different hydrocarbons. For those who might perhaps be in the dark, hydrocarbons are varying combinations of hydrogen and carbon molecules. Some common hydrocarbon gases include butane, isobutane, propane, methane, ethylene, butadiene, ethane, and propylene to mention but a few.
Let us now examine the different industrial and commercial applications of industrial gases.
Steel manufacturing and metal fabrication sector
Several industrial gases are used in both primary and fabricated metal production including steel and metal fabrication. In the particular case of steel manufacturing, oxygen is utilized as one of the primary raw materials for this critical process. Additionally, argon is utilized together with oxygen in refining stainless steel. Another industrial gas that plays a leading role in metal fabrication is acetylene which is utilized in numerous welding and metal cutting processes. While argon serves as a shielding gas in the electric arc welding of non-ferrous and specialty metals. Lastly, nitrogen plays an important role in heat-treating and metalworking products like metallic sheets, rods, casting, and wires.
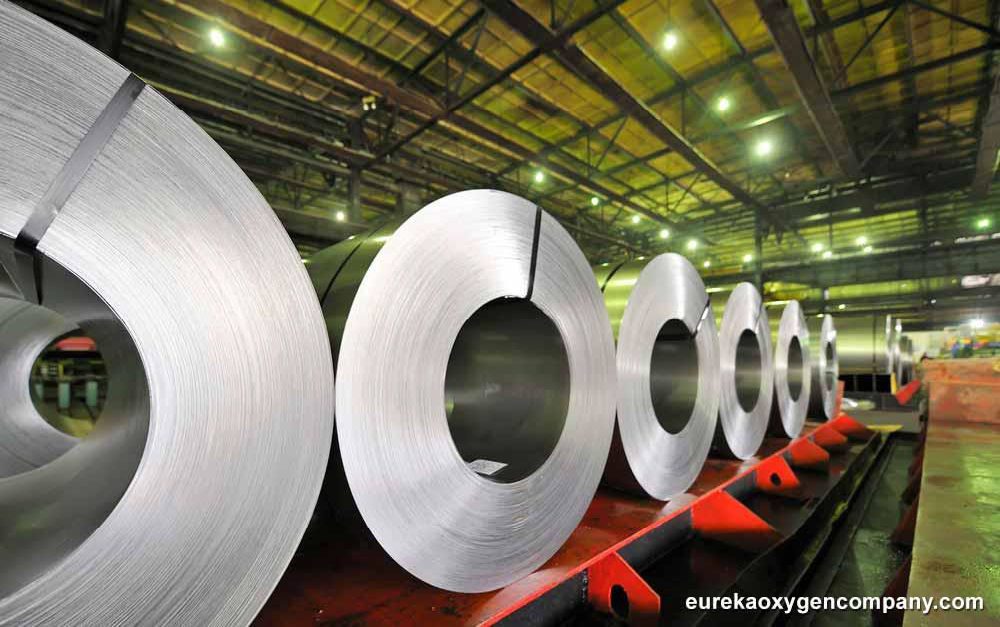

Manufacturing sector
Industrial gases such as argon, neon, xenon, nitrogen, and krypton are key ingredients in the manufacture of light bulbs. This group of gases is also used in the filling of gaps between double-glazing windows in the construction industry. This ensures modern buildings can be well insulated to become more energy efficient. Alternatively, gases such as hydrogen and nitrogen and their mixtures are utilized to heat-treat metals in order to induce hardness or other desirable physical properties.
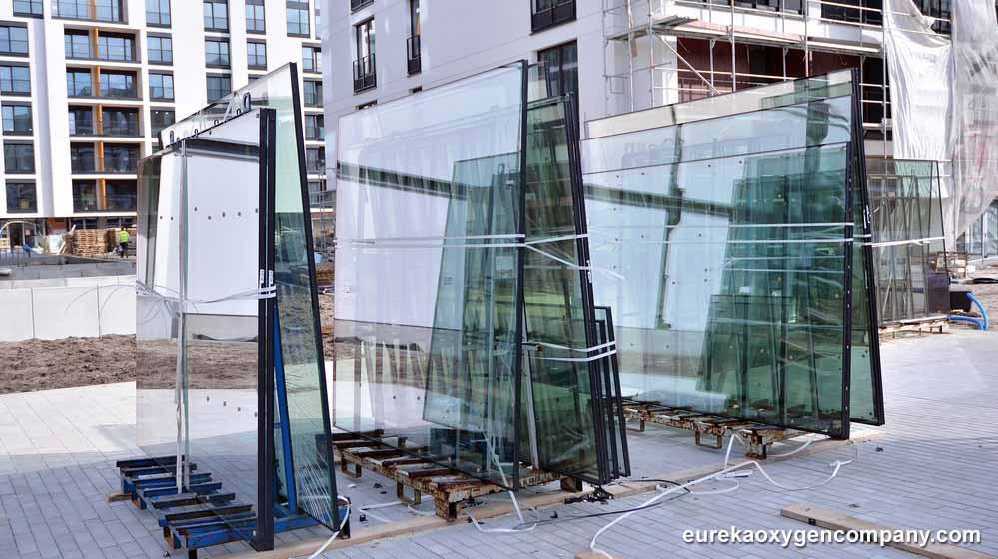

At the same time, quality control of diverse metals, plastics along with other raw materials is executed using a variety of industrial gases known as specialty gases. Specialty gases are as well utilized in testing the safety of numerous manufactured products. Some of the major tests of this kind that are conducted with gases include testing flammability and combustibility, which are performed with a number of high-purity gases and gas mixtures.
Food processing sector
A number of industrial gases are utilized to preserve the freshness of a wide variety of food products via different innovative processes. One excellent example is the modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) process. MAP happens to be an all-natural shelf-life prolonging technique which is used along with other methods like high pressure, microwave methods, and oxygen absorption. The ideal mixture of gases utilized in MAP enables foodstuff to retain its original flavor, texture, and appearance.
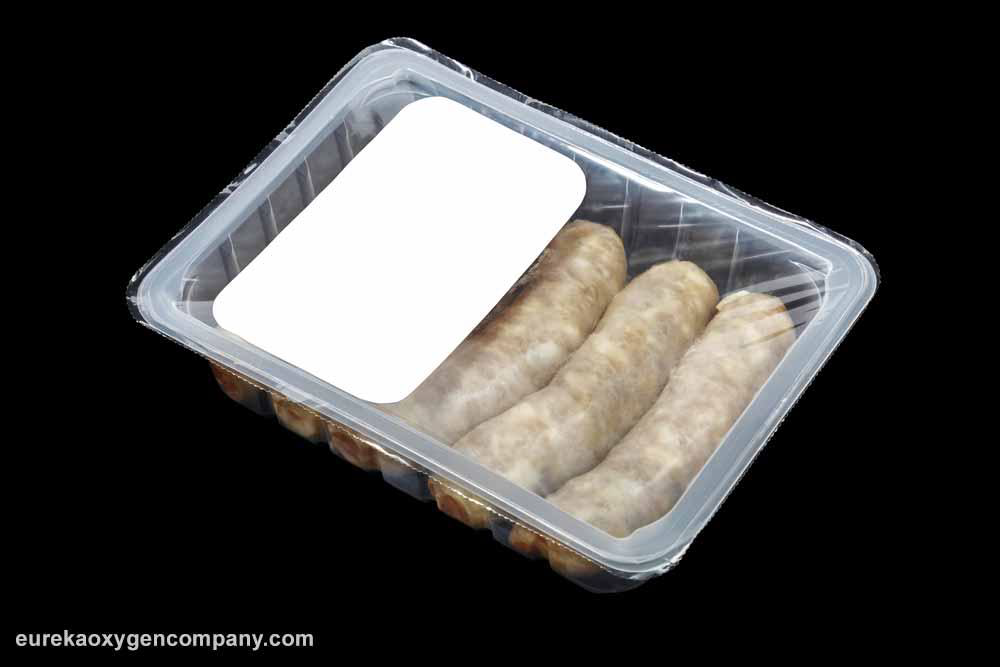

Gases such as carbon dioxide are utilized in the MAP process to inhibit microorganism growth in low-fat food products with high moisture content. Alternatively, inert nitrogen is used to preserve foodstuff with high-fat and low moisture content thanks to its excellent oxidation protection properties.
Eureka Oxygen is a leading provider of diverse industrial gases including #butane, #propane, #isobutane , #dryice and more. We also stock on the finest #welding equipment, supplies, PPE and accessories, industrial equipment and safety gear in the #humboldtcounty, #sooregon, #bayarea, and #northerncalifornia regions. #Choosehumboldt and #shopeureka today!